Over a quarter (25 percentage) of American seniors suffer from diabetes, which is a chronic disease that causes a variety of complications. According to one alarming figure, 10 to 15 percent patients with diabetes are plagued by foot and leg ulcers. If untreated, these seemingly innocuous injuries could become more severe and cause diabetic foot amputation. In reality, more than 80 percent of amputations originate from foot ulcers, underscoring the need for a rigorous prevention and care.
Managing diabetes is a multifaceted challenge, requiring a comprehensive approach that goes beyond the control of glucose. This is the reason that daily foot hygiene is a vital component in preventing the threat of diabetes-related complications.
Understanding the Landscape
It can be difficult to navigate the complex realm of diabetes complications. The prevalence of leg and foot ulcers in diabetic patients highlights the need for proactive care. With these stark figures, it is evident that the most effective way to prevent amputations is to foster a greater understanding.
The Amputation Conundrum
Amputation is a major threat for those with diabetes. It’s more than an occurrence. It impacts individuals directly. From minor cuts to the prospect that diabetic feet may require amputation, the journey is one of great stress.
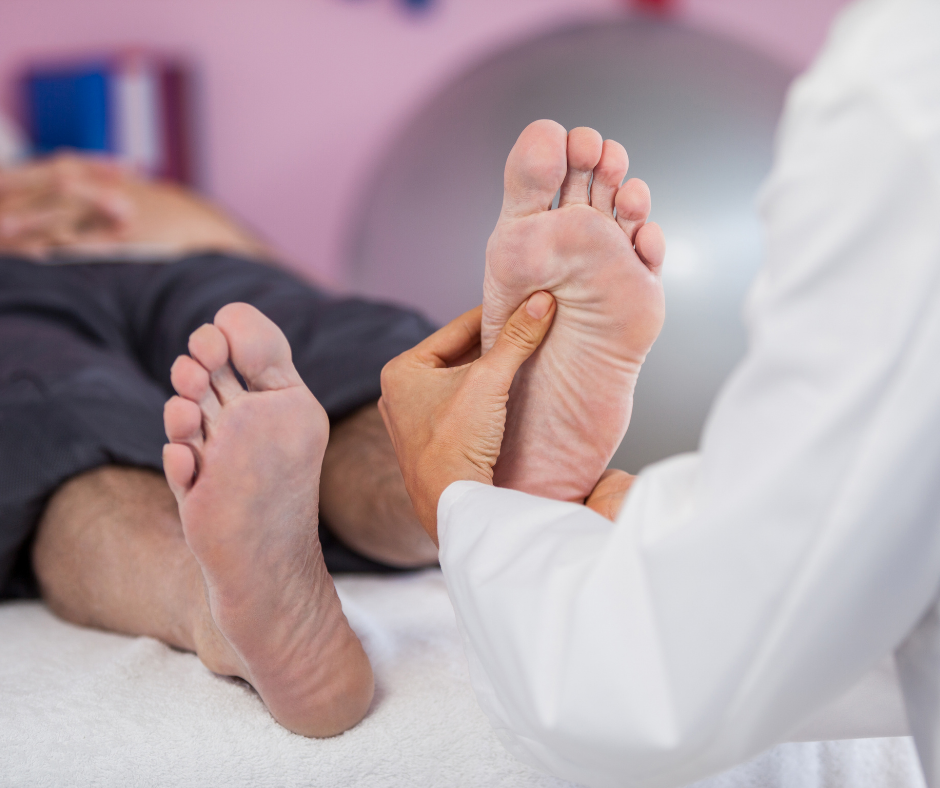
Daily Foot Care: A Protective Shield against Amputation
The foundation of diabetes amputation prevention lies in daily foot care. It’s more than an every-day foot care routine. It’s also a systematic approach to spot and fix potential issues before the problem gets worse. The daily routine covers everything from examining your feet for any injuries to moisturizing them properly.
Vascular Specialists: Their Role
While vascular specialists aren’t involved in the management of diabetes, they could contribute to reducing its complications. The purpose of treating patients is to improve blood flow to the lower extremities, which will reduce pain and promote healing. Through this collaborative approach the goal is clear: prevent diabetes-related amputations by mitigating the consequences of this condition.
Strategies for preventing Amputation
To be able to navigate the maze of diabetes amputation risk you require a combination of consciousness, vigilance and a skilled intervention. It is essential for those with diabetes to take an proactive attitude. Regular visits to medical professionals, including specialists in vascular surgery, can help with the early detection.
Leg Ulcers and Beyond Leg Ulcers: Triggers to Think About
The leg ulcers, frequently the precursors to more serious complications, require attention and knowledge. Understanding the triggers that contribute to the development of ulcers in the legs is a crucial step. Identifying the source for the ulcer, whether it’s poor circulation, neuropathy, or an amalgamation, allows for individualized and specific treatment.
Education as a means of empowerment
Empowering individuals with diabetes with information about the dangers and the preventive measures are essential. Initiatives to educate, both within healthcare facilities and in the general community, can create a bridge between knowledge and actions. Recognizing the potential effects of minor wounds could trigger early reactions that can prevent the amputation of a diabetic foot.
Battles between private parties, triumphs for the collective
The battle against diabetes-related complications isn’t an individual struggle; it’s a collective win. Joining support groups through your healthcare provider or in your local community is a good means to exchange experiences, gain insights and learn ways to cope. If you are faced with the possibility of an amputation the emotional burden can be a huge one. Support networks for communities provide support and peace.
In the end, the path through leg ulcers, diabetes, and the looming possibility of amputations are many-sided. The daily foot care is the initial line of defense. Vascular specialists’ expertise can be an invaluable asset to mitigate the effects. Patients with diabetes can lower the likelihood of amputations by promoting awareness, adopting preventive measures, and establishing an underlying support system.